According to the latest data from Similarweb, ChatGPT reached a record 390.5 billion visits in February 2025, a slight increase of 1.44% from January. Although growth slowed down month-on-month, year-on-year growth remained strong compared with February 2024, as high as 137%.
This continued growth has led ChatGPT to continue to climb in the global website rankings, currently ranked fifth among global desktop websites and seventh in combining desktop and mobile traffic. Data shows that ChatGPT accounts for 1.86% of global network traffic, with monthly visits of up to 4 billion, ranking among the top ten websites in the world, although there is still a gap compared with technology giants such as Google.
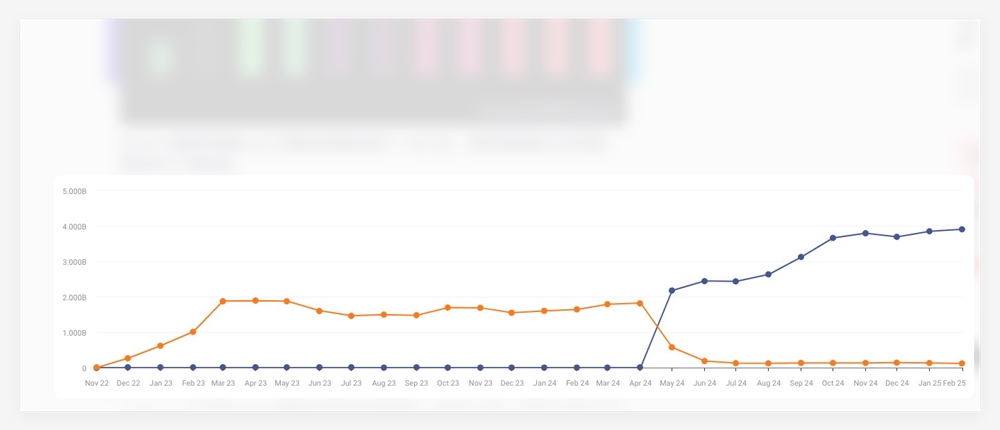
ChatGPT.com's traffic showed strong growth between the summer and autumn 2024, then flattened. The transition from orange to blue line indicates the transition to the new chatgpt.com domain. | Picture: Similarweb
ChatGPT's user base is also expanding rapidly. As of 2024, its number of paid users reached 15.5 million, a significant increase from 5.8 million at the beginning of the year. In contrast, although Chinese competitor Deepseek showed strong growth momentum, its daily website visits in January were 6.2 million, far lower than ChatGPT's 117.5 million in the same period.
However, Similarweb's data reveals a concern: Although ChatGPT has a huge user base, the outbound traffic generated is extremely sparse. In the United States, Reuters has received only 50,900 recommendations from ChatGPT over the past six months, ranking first among all news providers, followed by the New York Post (42,800) and the New York Times (31,600). Even the top 10 news websites combined, the total number of recommendations received in six months was less than 300,000.
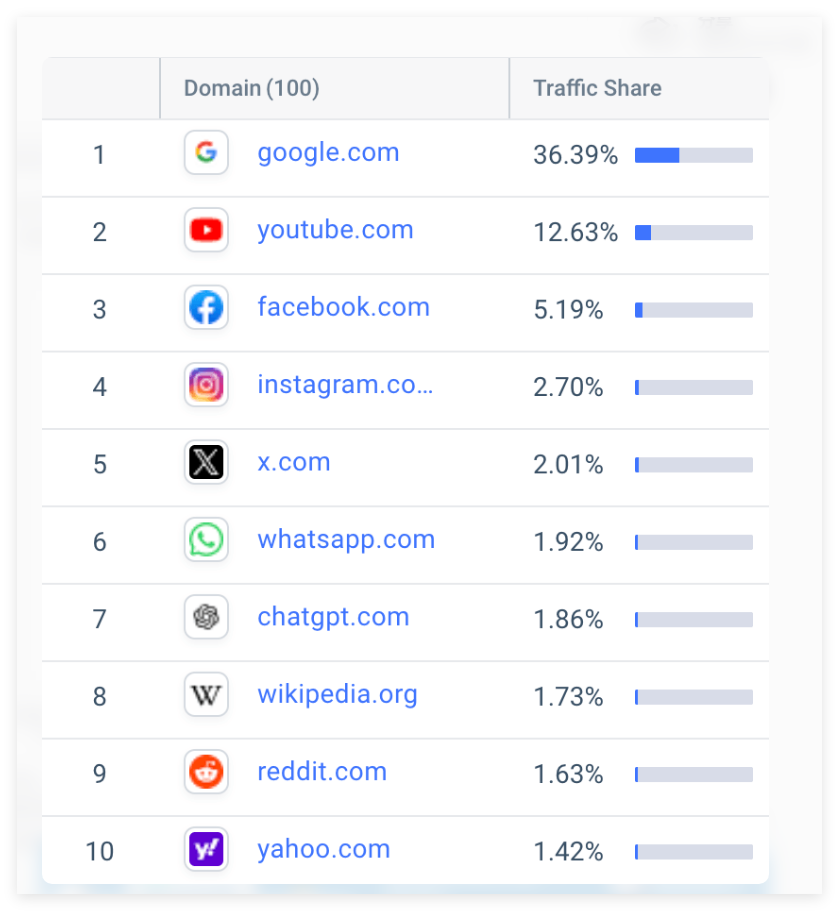
ChatGPT accounts for 1.86% of global network traffic and has reached 4 billion monthly visits, ranking among the top ten websites in the world, but still lags far behind Google and other tech giants. | Picture: Similarweb
A recent study found that 96% of AI answer engine users never clicked on the source link, which led to two serious problems: users cannot verify possible inaccurate information, and services such as ChatGPT search and Google's new AI search could undermine the traditional network ecosystem.
While OpenAI has partnered with multiple media to improve its content source, it is still rare for users to click on original content, and this minimal traffic sharing is raising concerns in the industry.