o1 in Medicine is an artificial intelligence model focused on the medical field, aiming to improve medical data processing capabilities and diagnostic accuracy through advanced language model technology. The model, developed by researchers at UC Santa Cruz, the University of Edinburgh, and the National Institutes of Health, demonstrated its potential for application in the medical field by testing on multiple medical data sets. The main advantages of the o1 model include high accuracy, multi-language support, and in-depth understanding of complex medical problems. The development background of this model is based on the current needs in the medical field for efficient and accurate data processing and analysis, especially in diagnosis and treatment recommendations. At present, the research and application of this model are still in the preliminary stage, but its application in medical education and clinical practice has broad prospects.
Demand group:
"The target audience is mainly medical researchers, clinicians and medical students. The o1 in Medicine model can help them process and analyze medical data more quickly and accurately, and provide more precise diagnostic suggestions and treatment plans. For medical researchers, The model can be used as a research tool to help them explore new medical problems and treatments; for clinicians, the model can assist diagnosis and provide treatment recommendations; for medical students, the model can be used as a learning tool to help them better understand complex medical concepts and cases."
Example of usage scenario:
On the NEJM problem, o1 provides a more concise and accurate reasoning process than GPT-4.
In the case of the Chinese dataset AI Hospital, o1 provides more accurate diagnosis and practical treatment recommendations than GPT-4.
In the multilingual task XmedBench, o1 demonstrated its application capabilities on medical data in different languages.
Product features:
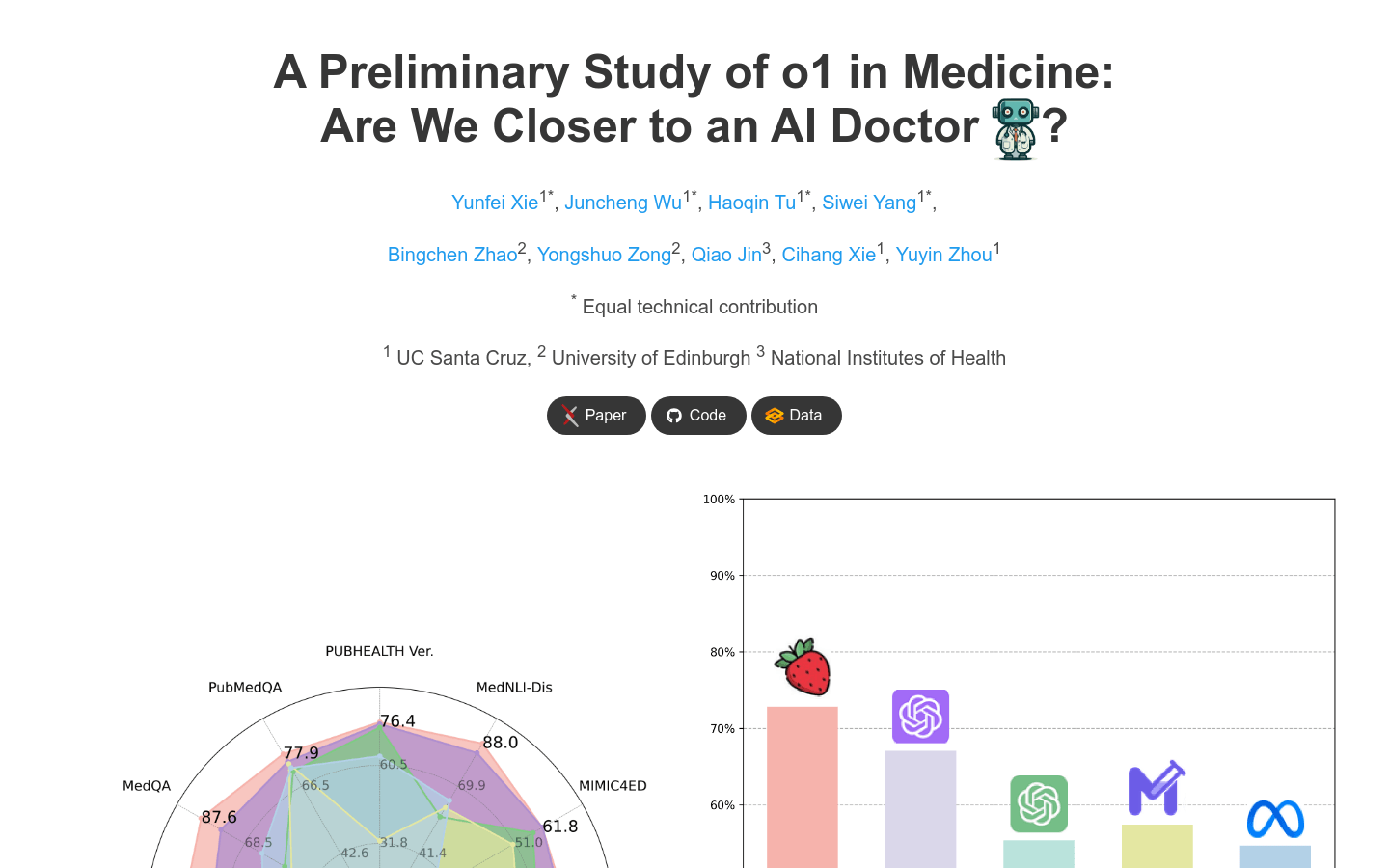
Demonstrated excellent performance on 12 datasets from different medical fields.
The average accuracy rate in 19 medical data sets reaches 73.3%.
Provides comprehensive model evaluation through different evaluation aspects, tasks, datasets, and prompting strategies.
Performs well on multilingual tasks and agent benchmarks.
On the knowledge question and answer data set, the model results with and without CoT prompts show differences.
Through case studies, the differences in question answers and diagnostic recommendations between o1 and GPT-4 are demonstrated.
Usage tutorial:
1. Visit o1 in Medicine ’s official website or GitHub page.
2. Read the introduction and research background of the model.
3. Download and install the necessary software and libraries to run the model locally or in the cloud.
4. Prepare medical data sets, including text, images, or other relevant formats, according to the guidance provided.
5. Use the model to train and test the data set and observe the performance and accuracy of the model.
6. Analyze the results output by the model and adjust model parameters or data sets as needed.
7. Apply the model to actual medical research or clinical practice, such as case analysis, diagnostic recommendations, etc.
8. Provide feedback to the development team based on usage experience to promote further improvement and development of the model.