Recently, the Evo2 bio-AI model jointly developed by Arc Institute and Nvidia was officially released. This basic model is based on DNA data from more than 100,000 organisms and aims to deeply decode various complex phenomena in biology. Evo2 can identify patterns that researchers have taken years to discover in the gene sequences of different organisms, greatly improving the recognition of disease-related mutations and designing a new genome that is comparable to simple bacteria.
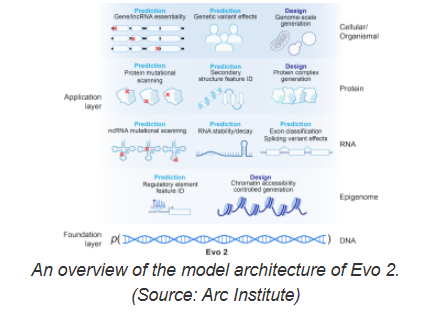
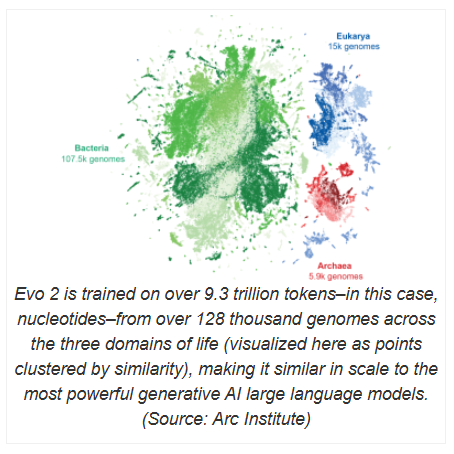
Evo2 training involves processing of more than 93 trillion nucleotides, far exceeding its predecessor, Evo1. Its development team comes from Nvidia and Arc Institute, a nonprofit biomedical research organization based in Palo Alto, California, and works closely with researchers at Stanford University, UC Berkeley and UC San Francisco. Evo2 not only has strong computing power, but also actively explores transparency and interpretability. To make scientific research more open, the research team also disclosed Evo2's training data, code and model weights, marking it as the largest fully open source biological AI model to date.
Patrick Hsu, co-founder of the Arc Institute and assistant professor at UC Berkeley, said the development of Evo2 is an important breakthrough in the field of generative biology. Through this technology, machines can "read", "write" and "think" the language of nucleotides, which has promoted the progress of biological research. Evo2's training capabilities are comparable to large-scale language models, showing strong potential in predicting disease mutations and designing potential artificial life.
In addition, Evo2 can also provide new ideas for the design of biological therapies, such as gene therapy for activation of specific cell types, to reduce side effects and improve treatment accuracy. The development of Evo2 is not only a technological breakthrough, but also has a profound impact on understanding of biology.
Data on pathogens that infect humans and other complex organisms were specifically ruled out when researchers ensured that the model was developed responsibly. Anthony Costa, director of digital biology at Nvidia, said Evo2 breaks through the limitations of the basic biological model and provides scientists around the world with powerful collaborative tools to address the major health and disease challenges facing humanity.